トピックス
ナノ粒子合成のためのカスタムメイド樹状フェニルアゾメチン
2022.03.18
K. Albrecht, M. Taguchi, T. Tsukamoto, T. Moriai, N. Yoshida, K. YamamotoChem. Sci. 2022, 13, 5813-5817.
特定の原子数を持つ金属クラスターを準備規模で合成して高度な特性を研究することは依然として課題である。デンドリマーテンプレート法は、サイズや原子数を制御したナノ粒子を合成するための強力な方法であるが、従来のデンドリマーではすべての原子数にアクセスすることはできない。この問題に対処するために、限られた数の配位サイト(n = 16)と非配位性の大きなポリフェニレンシェルを持つ新しいカスタムメイドのフェニルアゾメチンデンドリマー(DPA)が設計された。非対称デンドロンとアダマンタンコアの四置換デンドリマー(PPDPA16)は、成功裏に合成された。配位挙動により、PPDPA16に16個の金属ルイス酸(RhCl3、RuCl3、およびSnBr2)が蓄積されることが確認された。複合体の還元後、制御されたサイズの低原子価金属ナノ粒子が得られた。このカスタムメイドのデンドリマーは、望ましい原子性を持つさまざまな金属クラスターを合成するための有望なアプローチである。
Poly-phenylene jacketed tailor-made dendritic phenylazomethine ligand for nanoparticle synthesisSynthesizing metal clusters with a specific number of atoms on a preparative scale for studying advanced properties is still a challenge. The dendrimer templated method is powerful for synthesizing size or atomicity controlled nanoparticles. However, not all atomicity is accessible with conventional dendrimers. A new tailor-made phenylazomethine dendrimer (DPA) with a limited number of coordination sites (n = 16) and a non-coordinating large poly-phenylene shell was designed to tackle this problem. The asymmetric dendron and adamantane core four substituted dendrimer (PPDPA16) were successfully synthesized. The coordination behavior confirmed the accumulation of 16 metal Lewis acids (RhCl3, RuCl3, and SnBr2) to PPDPA16. After the reduction of the complex, low valent metal nanoparticles with controlled size were obtained. The tailor-made dendrimer is a promising approach to synthesize a variety of metal clusters with desired atomicity.
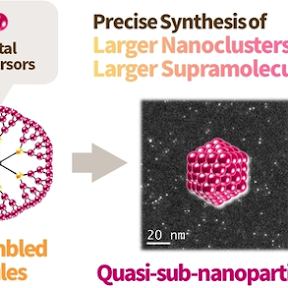
デンドロン組立超分子テンプレートによる準サブナノ粒子の高精度合成
2022.01.10
T. Tsukamoto, K. Tomozawa, T. Moriai, N. Yoshida, T. Kambe, K. YamamotoAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114353.
準サブナノ材料(1~3 nm)は、バルク固体と分子の両方と見なされるグレイ構造に由来する独自の特性を示すと予測されているが、その合成は非常に困難である。本研究では、配位化学と高分子化学の組み合わせを用いた準サブナノサイズ材料の新しいテンプレート合成法を説明する。ホスト酸性コアユニットに6つのトリチリウムカチオンを持つゲスト塩基性フェニルアゾメチンデンドロンユニットの自己組織化を利用し、デンドロン組立超分子を簡便かつ定量的に高価な技術を使わずに構築した。この巨大な超分子カプセルは、塩基性リガンド内に複数の酸性ロジウム塩を蓄積し、多核錯体の形成を介してロジウム粒子の精密合成を可能にした。得られた粒子(Rh84, 約1.5 nm)は、1~3 nmの範囲内の粒子サイズを持ち、従来のサブナノ粒子(Rh14, 約0.85 nm)よりも大きく、準サブナノ粒子の精密なテンプレート合成が成功したことを実証した。
Highly Accurate Synthesis of Quasi-sub-nanoparticles by Dendron-assembled Supramolecular TemplatesQuasi-sub-nanomaterials (1–3 nm) have been predicted to exhibit unique properties originating from the gray structures considered both bulk solids and molecules, while their synthesis is extremely difficult. The present study describes a new template synthesis method for quasi-sub-nanosized materials using a combination of coordination chemistry and polymer chemistry. Utilizing self-assembly of guest basic phenylazomethine dendron units onto host acidic core units with six tritylium cations, the dendron-assembled supramolecules were constructed easily and quantitatively without costly techniques. This huge supramolecular capsule accumulating multiple acidic rhodium salts in its basic ligands enabled a precise synthesis of rhodium particles via formation of multinuclear complexes. The obtained particles (Rh84, ≈1.5 nm) have particle sizes within 1–3 nm range and were larger than conventional sub-nanoparticles (Rh14, ≈0.85 nm), therefore the precise template synthesis of quasi-sub-nanoparticles was successfully demonstrated.
中心の銀が白金サブナノクラスターの室温燐光を18倍に向上
2020.11.07
Y. Akanuma, T. Imaoka, H. Sato, K. YamamotoAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4551-4554.リガンドで保護された金属ナノクラスターの発光における金属コア(金属-金属相互作用)とシェル(金属-リガンド相互作用)の役割については議論が続いている。我々は、白金-チオレート錯体およびその銀イオン包含錯体(銀ドープ白金サブナノクラスター)の凝集誘起室温燐光を発見した。銀イオンの包含により、発光量子収率が18倍に向上した。光物理的測定では、銀ドープ白金サブナノクラスターの非放射減衰速度が遅くなることが示された。DFT計算により、主にAgのs軌道とPtのd軌道からなるLUMOが、励起状態での構造歪みを抑制する重要な役割を果たしていることが明らかになった。この研究は、原子レベルで精密に制御された多金属発光ナノクラスターの分子軌道に基づいた設計戦略の研究を刺激することを期待している。Silver in the Center Enhances Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of a Platinum Sub-nanocluster by 18 Times
There has been controversy surrounding the roles of the metal core (metal–metal interaction) and the shell (metal–ligand interaction) in photoluminescence of ligand-protected metal nanoclusters. We have discovered aggregation-induced room-temperature phosphorescence of a platinum–thiolate complex and its silver ion inclusion complex (a silver-doped platinum sub-nanocluster). The inclusion of silver ion boosted the photoluminescent quantum yield by 18 times. Photophysical measurements indicate that the rate of nonradiative decay was slower for the silver-doped platinum sub-nanocluster. DFT calculations showed that the LUMO, which had the main contribution from Ag s-orbital and Pt d-orbitals, played a critical role in suppressing the structural distortion at the excited state. This work will hopefully stimulate more research on designing strategies based on molecular orbitals of atomicity-precise luminescent multimetallic nanoclusters.
異なる原子数の順次スクリーニング技術による量子材料探索
2020.09.08
T. Tsukamoto, A. Kuzume, M. Nagasaka, T. Kambe, K. YamamotoJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19078-19084.サブナノ粒子(SNPs)は、極めて小さい粒子サイズが量子スケールにまで及ぶため、独自の特性と機能を示す。SNPsの合成には、原子性と組成の精密な制御が必要とされるが、これまでその達成は困難であった。私たちは最近、マクロ分子テンプレートを使用してこのような原子レベルの制御を実現する「原子ハイブリッド化法(AHM)」を開発した。革新的な量子材料の探求において、次のステップは機能的なサブナノ材料の実用的な創出が中心課題となる。本研究では、最新のAHMを用いて、順次組成を持つ単純なインジウム-スズ二元系に注目し、機能性SNPsの新しいスクリーニング技術を確立した。その結果、特定の組成でのみ熱力学的に不安定なインジウム種が生成され、耐久性のある発光機能をもたらすことが明らかになった。このようなサブナノサイズの物質における現象は、未知の量子材料の分野の発展において重要な役割を果たすであろう。
Quantum Materials Exploration by Sequential Screening Technique of Heteroatomicity
Subnanoparticles (SNPs) exhibit unique properties and functions due to their extremely small particle sizes which extend into the quantum scale. Although the synthesis of SNPs requiring precise control of atomicity and composition has not been accomplished, we recently developed an atom-hybridization method (AHM) that realizes such atomic-level control using a macromolecular template. As a next step in the quest for innovative quantum materials, the practical creation of functional subnanomaterials will become a central subject. In this study, we established a new screening technique for functional SNPs by focusing on the simple indium–tin binary system with sequential compositions using the latest AHM. As a result, it was revealed that a thermodynamically unstable indium species was produced only at a certain composition leading to a durable luminescent function. Such a phenomenon in subnanosized substances will play an important role in the development of the as-yet-unknown field of quantum materials.
貴金属多金属1ナノメートル触媒によるオレフィンの選択的ヒドロペルオキシド化の実現
2020.08.26
T. Moriai, T. Tsukamoto, M. Tanabe, T. Kambe, K. YamamotoAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23051-23055.
サブナノメートル(約1 nm)スケールの粒子科学は、世界中の注目を集めている。しかし、サブナノ粒子(SNPs)の精密な合成の技術的難しさのため、未踏の領域であった。最近、適切に設計されたマクロ分子をテンプレートとして使用することにより、SNPsを精密に合成する「原子ハイブリッド化法(AHM)」を開発した。現在、AHMによって得られた合金SNPsの化学反応性を調査した。貴金属元素に注目し、これらのSNPsが触媒するオレフィンの酸化反応を系統的に評価した。SNPsは、従来の触媒よりも穏やかな条件下でも高い触媒性能を示した。さらに、複数の元素のハイブリッド化により、ヒドロペルオキシド誘導体の形成に対するターンオーバー周波数と選択性が向上した。材料の小型化とハイブリッド化の観点から、一般に不安定なヒドロペルオキシドを提供するユニークな量子サイズ触媒について議論する。
Selective Hydroperoxygenation of Olefins Realized by a Coinage Multimetallic 1-Nanometer CatalystThe science of particles on a sub-nanometer (ca. 1 nm) scale has attracted worldwide attention. However, it has remained unexplored because of the technical difficulty in the precise synthesis of sub-nanoparticles (SNPs). We recently developed the “atom-hybridization method (AHM)” for the precise synthesis of SNPs by using a suitably designed macromolecule as a template. We have now investigated the chemical reactivity of alloy SNPs obtained by the AHM. Focusing on the coinage metal elements, we systematically evaluated the oxidation reaction of an olefin catalyzed by these SNPs. The SNPs showed high catalytic performance even under milder conditions than those used with conventional catalysts. Additionally, the hybridization of multiple elements enhanced the turnover frequency and the selectivity for the formation of the hydroperoxide derivative. We discuss the unique quantum-sized catalysts providing generally unstable hydroperoxides from the viewpoint of the miniaturization and hybridization of materials.
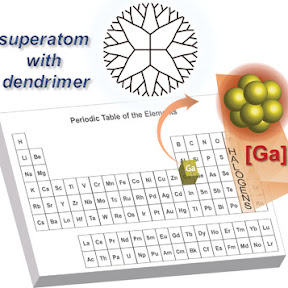
デンドリマー内の超原子ガリウムクラスター:原子数に依存する独自の剛性と反応性
2020.02.21
T. Kambe, A. Watanabe, M. Li, T. Tsukamoto, T. Imaoka, K. YamamotoAdv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907167.
超原子は他の元素の代替としての可能性があるため、研究されてきた。超原子の溶液相合成は、その利用可能性を実現するために注目を集めている。しかし、従来のアプローチは基本的に単一クラスターの形成に限られていた。ここでは、超原子を調査し、これらの超原子内の原子価電子の数を、存在するガリウム原子の数を設計することで変化させた。デンドリマーテンプレート法に基づいて、3、12、13、およびその他の数の原子からなるクラスターが合成された。Ga13のハロゲンのような超原子特性は、他のクラスターとは全く異なる構造的および電気化学的な観察によって明らかにされた。2Pおよび1P超原子軌道をそれぞれ満たすことができる13および3原子のガリウムクラスターは、異なる反応性を示す。3原子のガリウムクラスターは、未占有軌道のエネルギーレベルの低下によりGa3H2−に還元されることが示唆されている。これらのガリウムクラスターの結果は、超原子の候補を提供する。
Superatomic Gallium Clusters in Dendrimers: Unique Rigidity and Reactivity Depending on their AtomicitySuperatoms have been investigated due to their possible substitution for other elements. The solution-phase synthesis of superatoms has attracted attention to realize the availability of superatoms. However, the previous approach is basically limited to the formation of a single cluster. Here, superatoms are investigated and the number of valence electrons in these superatoms is changed by designing the number of gallium atoms present. Based on the dendrimer template method, clusters consisting of 3, 12, 13, and other numbers of atoms have been synthesized. The halogen-like superatomic nature of Ga13 is structurally and electrochemically observed as completely different to the other clusters. The gallium clusters of 13 and 3 atoms, which can fill the 2P and 1P superatomic orbitals, respectively, exhibit different reactivities. The 3-atom gallium cluster is suggested as being reduced to Ga3H2− due to the lower shift of energy levels in the unoccupied orbitals. The results for these gallium clusters provide candidates for superatoms.
多金属クラスター合成のための原子ハイブリッド化
2018.10.30
T. Tsukamoto, T. Kambe, A. Nakao, T. Imaoka, K. Yamamoto
Nature Commun. 2018, 9, 3873.
多元合金ナノ粒子の新たな合成手法を開発
サブナノメートルスケールの金属クラスターの化学は、特に多金属クラスターにおいて、サイズと組成を制御して合成することが難しいため、まだ十分に理解されていない。多金属サブナノクラスターのテンプレート合成は、マクロ分子テンプレートとしてフェニルアゾメチンデンドリマーを使用することによって達成される。その分子内ポテンシャル勾配により、最大8元素を含む金属前駆体複合体をテンプレート上に正確に取り込むことが可能である。この方法の有用性は、5元素(Ga1In1Au3Bi2Sn6)から成る多金属サブナノクラスターを合成することで実証されている。このクラスターのサイズと組成は正確に制御され、関与する金属は互いに合金化される。このアプローチは、異なる金属をさまざまな組み合わせで簡単にブレンドし、サブナノメートルスケールの新しい材料を作成する能力を提供し、化学の分野における新しい領域の発展につながるであろう。
Atom-hybridization for Synthesis of Polymetallic ClustersThe chemistry of metal clusters on the sub-nanometer scale is not yet well understood because metal clusters, especially multimetallic clusters, are difficult to synthesize with control over size and composition. The template synthesis of multimetallic sub-nanoclusters is achieved using a phenylazomethine dendrimer as a macromolecular template. Its intramolecular potential gradient allows the precise uptake of metal precursor complexes containing up to eight elements on the template. The usefulness of this method is demonstrated by synthesizing multimetallic sub-nanoclusters composed of five elements (Ga1In1Au3Bi2Sn6). The size and composition of this cluster can be precisely controlled and the metals involved are alloyed with each other. This approach provides the ability to easily blend different metals in various combinations to create new materials on the sub-nanometer scale, which will lead to the development of a new area in the field of chemistry.
Al13−超原子の液相合成
2017.12.11
T. Kambe, N. Haruta, T. Imaoka, K. Yamamoto
Nature Commun. 2017, 8, 2046.
超原子、すなわちそれらが構成される元素とは異なる特性を模倣するクラスターは、調整可能な特性を持つ前例のない材料の構築ブロックとして機能する可能性がある。超原子の溶液相合成法の開発は、この研究分野の将来の進展に不可欠な成果となるであろう。ここでは、デンドリマーテンプレートを用いて溶液中でアルミニウムクラスター(最もよく知られたスーパ―アトムであるAl13−)を生成する方法を報告する。Al13−クラスターは、質量分析および走査透過型電子顕微鏡を使用して同定され、X線光電子分光法により結合エネルギーが測定される。Al13−の超原子安定性は、その酸化傾向を評価することで示される。さらに、溶液中でのAl13−の合成は電気化学測定を可能にし、その結果はAl13−の酸化を示唆している。この溶液相合成法は、クラスター科学の実験的発展において重要な役割を果たす。
Solution-phase synthesis of Al13− using a dendrimer template
Superatoms, clusters that mimic the properties of elements different to those of which they are composed, have the potential to serve as building blocks for unprecedented materials with tunable properties. The development of a method for the solution-phase synthesis of superatoms would be an indispensable achievement for the future progress of this research field. Here we report the fabrication of aluminum clusters in solution using a dendrimer template, producing Al13−, which is the most well-known superatom. The Al13− cluster is identified using mass spectrometry and scanning transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is used to measure the binding energies. The superatomic stability of Al13− is demonstrated by evaluating its tendency toward oxidation. In addition, the synthesis of Al13− in solution enables electrochemical measurements, the results of which suggest oxidation of Al13−. This solution-phase synthesis of Al13− superatoms has a significant role for the experimental development of cluster science.
原子数明確な白金クラスター担持触媒の大量合成
2017.09.25
T. Imaoka, Y. Akanuma, N. Haruta, S. Tsuchiya, K. Ishihara, T. Okayasu, W.-J. Chun, M. Takahashi, K. Yamamoto
Nature Commun. 2017, 8, 688.
サブナノメートルの貴金属クラスターは、特に触媒用途において非常に大きな可能性を秘めている。わずか1つの原子の違いがその反応性に大きな変化を引き起こすため、原子レベルの精度での調製方法が不可欠である。このような精度がガス相合成によって達成されているが、大規模な調製は依然として最前線にあり、実用的な応用を妨げている。我々は、ティアラ状の白金複合体(リング数 n=5–13)からミリグラムスケールでの白金クラスターの原子精度かつ完全にスケーラブルな合成を示す。水素流中での炭素支持体上の複合体の低温焼成により、前駆体複合体と同じ原子性を持つ単分散の白金クラスターが得られる。これらのクラスターのうち、Pt10クラスターは他のクラスターに比べてスチレンの水素化において高い触媒活性を示す。この方法は、これらのクラスターを調製スケールの触媒作用に応用するための道を開く。
Platinum clusters with precise numbers of atoms for preparative-scale catalysis
Subnanometer noble metal clusters have enormous potential, mainly for catalytic applications. Because a difference of only one atom may cause significant changes in their reactivity, a preparation method with atomic-level precision is essential. Although such a precision with enough scalability has been achieved by gas-phase synthesis, large-scale preparation is still at the frontier, hampering practical applications. We now show the atom-precise and fully scalable synthesis of platinum clusters on a milligram scale from tiara-like platinum complexes with various ring numbers (n = 5–13). Low-temperature calcination of the complexes on a carbon support under hydrogen stream affords monodispersed platinum clusters, whose atomicity is equivalent to that of the precursor complex. One of the clusters (Pt10) exhibits high catalytic activity in the hydrogenation of styrene compared to that of the other clusters. This method opens an avenue for the application of these clusters to preparative-scale catalysis.
溶媒を使用しない炭化水素の好気的酸化のための精密に制御された多金属ナノクラスター触媒
2017.07.26
M. Takahashi, H. Koizumi, W. Chun, M. Kori, T. Imaoka, K. Yamamoto
Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700101.
合金ナノ粒子の触媒活性は、粒子サイズと異なる金属の組成比に依存する。Pd、Pt、およびAuからなる合金ナノ粒子は、酸化反応の触媒として広く使用されている。酸化反応におけるPtおよびAuナノ粒子の触媒活性は、粒子サイズが小さくなるほど増加し、合金ナノ粒子の金属間界面で増加することが知られている。したがって、直径約1 nmの多金属ナノクラスター(MNCs)は酸化反応の触媒としての可能性を持つ。しかし、均一な合金ナノクラスターの調製に関する報告はほとんどない。我々は、塩基性の勾配を持つ配位サイトを備えた高分子テンプレートを使用して、精密に制御されたMNCs(約1 nm)を合成する方法を報告する。グラファイト化されたメソポーラス炭素に支持されたCu-Pt-Au MNCsは、炭化水素の好気的酸化において市販のPt触媒の24倍の触媒活性を示すことを明らかにした。さらに、炭化水素をケトンに変換する溶媒を使用しない好気的酸化反応を、少量のラジカル開始剤を用いて常温で行うことに成功し、これは初めての固体触媒による反応である。
Finely controlled multimetallic nanocluster catalysts for solvent-free aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons
The catalytic activity of alloy nanoparticles depends on the particle size and composition ratio of different metals. Alloy nanoparticles composed of Pd, Pt, and Au are widely used as catalysts for oxidation reactions. The catalytic activities of Pt and Au nanoparticles in oxidation reactions are known to increase as the particle size decreases and to increase on the metal-metal interface of alloy nanoparticles. Therefore, multimetallic nanoclusters (MNCs) around 1 nm in diameter have potential as catalysts for oxidation reactions. However, there have been few reports describing the preparation of uniform alloy nanoclusters. We report the synthesis of finely controlled MNCs (around 1 nm) using a macromolecular template with coordination sites arranged in a gradient of basicity. We reveal that Cu-Pt-Au MNCs supported on graphitized mesoporous carbon show catalytic activity that is 24 times greater than that of a commercially available Pt catalyst for aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons. In addition, solvent-free aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons to ketones at room temperature, using small amounts of a radical initiator, was achieved as a heterogeneous catalytic reaction for the first time.